Recently, a prominent industry media organization, Drug Hunter, has published their list of the
top 10 small molecule medications for 2023, which was compiled from hundreds of research publications. Preclinical non-hormonal male contraceptives, the first novel deuterated API to receive approval, four first-in-class medications, and more are among them.
Deucravacitinib is the only TYK2 inhibitor currently approved globally and is thought to be a new potential standard of care. It is also the first oral treatment for plaque psoriasis following the 2017 approval of deutetrabenazine. Deucravacitinib is the second deuterium-generation drug and is anticipated to be the next high-profile product for BMS.

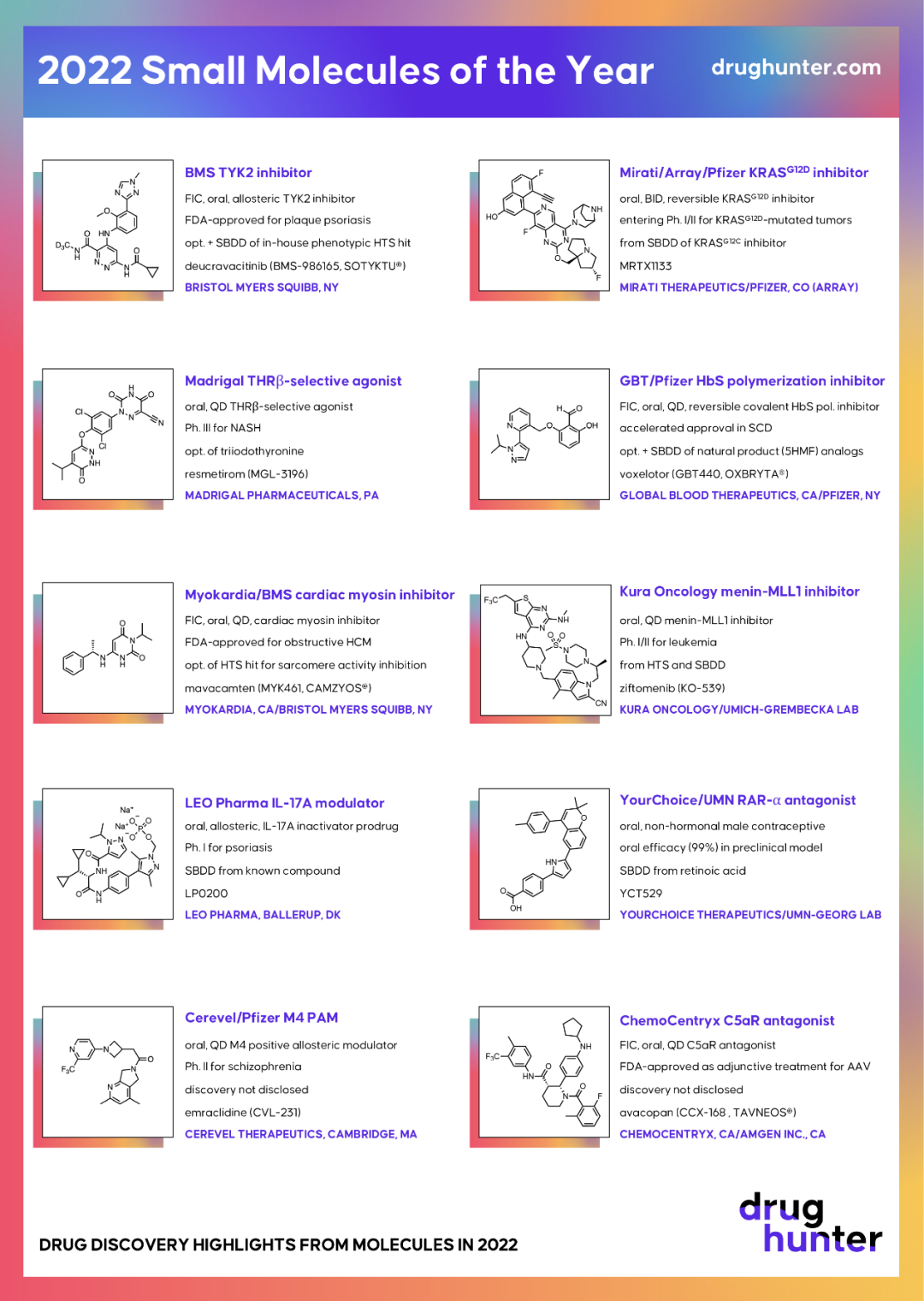
A reversible non-covalent long-acting KRASG12D inhibitor called
MRTX1133(CAS 2621928-55-8) was created by Mirati Therapeutics and is presently undergoing clinical testing as an oral cancer treatment.
The first KRAS inhibitors were just recently become available despite the fact that mutant KRAS proteins are widely recognized to be the cause of cancer. The most dangerous, challenging, and frightening cancer-causing mutations are KRAS mutations. The majority of targeted medications have failed in front of it during the past 40 years, serving as the "nail in the coffin" of targeted therapy.
The outcomes of a preclinical examination of the KRAS G12D-targeted drug MRTX1133 by a research team from Mirati Therapeutics were released in Nature Medicine. Researchers assessed the anti-tumor effectiveness and mode of action of MRTX1133 in this study. The observations highlight the therapeutic sensitivity and wide-ranging dependency of KRAS G12D mutation-positive tumors on mutant KRAS for tumor cell proliferation and survival. They also show the viability of selective targeting of KRAS mutants with non-covalent, high-affinity small molecules.
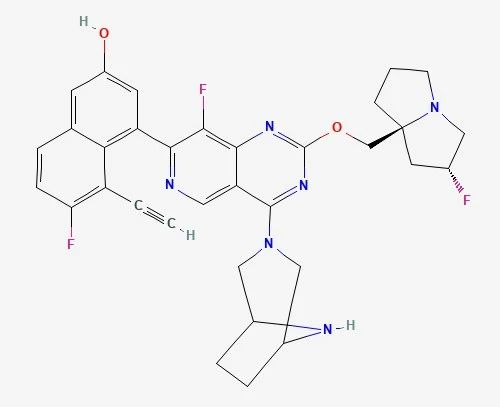
Resmetirom(CAS 920509-32-6) is an oral THR-selective agonist that targets the liver and is used once daily to imitate the effects of thyroid hormones on hepatic lipid metabolism and hepatic fat reduction. It was first developed by Roche. Madrigal acquired the drug's worldwide development rights in 2008.
Resmetirom's Phase 3 clinical study for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), MAESTRO-NASH, was successful in meeting its primary goal and important secondary endpoints, according to a statement released by Madrigal Pharmaceuticals on December 19, 2022. In contrast to placebo, NASH retreated following Resmetirom treatment in 316 participants' biopsies without increasing fibrosis.
Resmetirom, for which Madrigal will file an NDA in 2023, is anticipated to be the first brand-new medication for NASH to be authorized in recent years.
Four Phase 3 clinical studies for the medication are presently underway. Results from the MAESTRO-NASH Phase 3 clinical trial have previously shown LDL-C reduction (80 mg: -12%, p0.0001; 100 mg: -16%, p0.0001; placebo: 1%), NASH remission (80 mg: 26%, p0.0001; 100 mg: 30%, p0.0001; placebo: 10%), and improved fibrosis in two dose groups of resmetirom compared to the placebo group.
NASH has a vast patient population and is one of the most important unmet needs in healthcare today, however there are no FDA, EMA, or NMPA-approved medications available. The majority of the approximately 20 targets that are the focus of the hundreds of medications that are now being developed worldwide include PPAR, THR-, GLP-1, FXR, FGF21, etc.
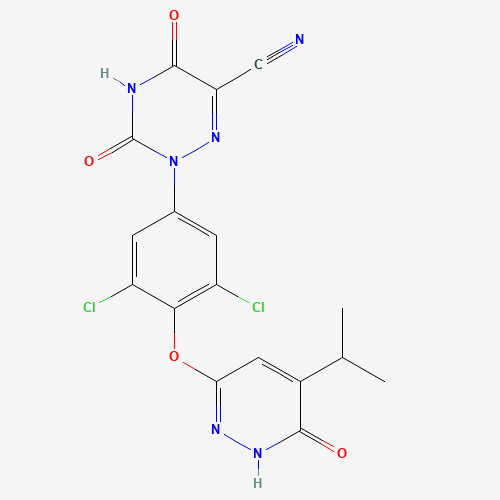
By reducing hemoglobin aggregation, a significant contributor to sickle cell illness, Global Blood Therapies (GBTfirst-in-class )'s reversible covalent aldehyde,
Voxelotor (Oxbryta) (CAS 1446321-46-5), directly tackles the underlying etiology of sickle cell disease (SCD).
Three months before the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) planned deadline, Voxelotor was granted accelerated FDA clearance in November 2019 for the treatment of hemolytic anemia in pediatric and adult patients with SCD who are 12 years old.
Voxelotor had previously been given Priority Drug Status (PRIME) and Orphan Drug designation by the EMA for the management of SCD.
As the first oral medication to raise hemoglobin levels and prevent hemolysis in sickle cell disease, the advent of voxelotor represents a turning point in the treatment of SCD. A larger percentage of participants (51%) in the 1500 mg Voxelotor dose group than in the placebo dosing group at 24 weeks had a hemoglobin response (incremental adverse effects above 1.0 g/dL) in the pivotal phase III HOPE study, which included 274 participants. Hemoglobin concentrations showed consistent improvement after a 72-week follow-up study.

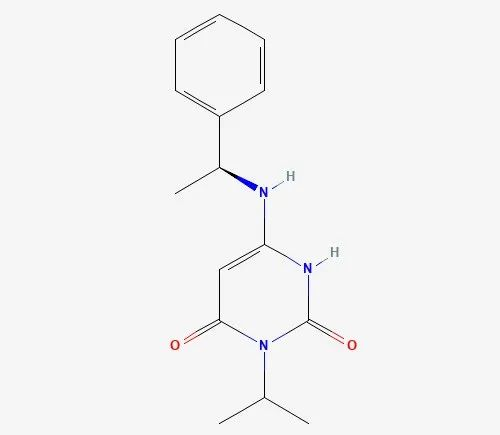
Mavacamten (Camzyos)(CAS 1642288-47-8), a novel, oral-selective inhibitor of the cardiac myocardial variant, was created by Myokardia and will be purchased by Bristol-Myers Squibb for up to $13.1 billion in 2020.
Mavacamten from BMS was given FDA approval on April 28, 2022, for the treatment of adult patients with symptomatic obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM) and cardiac function classes II–III in order to enhance patient function and symptoms.
Mavacamten has changed patients' lives because there were no disease-modifying medicines for HCM prior to its release. The study on the actions of kinesins, myosin, and actin at Jim Spudich's lab at Stanford University is where mavacamten's scientific origins may be found. Spudich co-founded Cytokinetics in 1998; now, it is a $4 billion publicly traded firm.
The "Molecular Drug of the Month" for September 2022 is ziftomenib, which prevents the menin and mixed-spectrum leukemia (MLL) fusion proteins from interacting in a way that promotes the growth of various leukemias.
Early results from a current Phase I/II clinical study for acute leukemia showed six patients had responses, and two patients who had received extensive pretreatment had full responses. Due to a patient's death in November 2021, which may have been connected to the differentiation syndrome, some of the clinical work done for this experiment was placed on hold and later discontinued. As a result of tissue injury, differentiation syndrome is a well-known adverse occurrence.
It is important to note that
Revumenib, a different medication in this sector with Phase I trial findings released in the same time period last year (November 2022), also has a strong safety profile with CR/CRh rates and ORR rates of 30% and 59%, respectively. Several international businesses are now pursuing this goal, while local players Janssen and Shanghai Yehui Pharmaceuticals are also involved in the plan. The menin inhibitor being developed by Yehui Pharmaceuticals is still in the preclinical stage, and no patent has been declared. The field is still in the clinically inactive stage and is anticipating the early introduction of the medication that will give sufferers hope.

LEO Pharma finished LP0200's Phase 1 clinical research, which examined the drug's safety in healthy volunteers, in August 2022.
IL-17 has long been a well-liked target in the field of immunology due to the clinical and commercial success of marketed drugs like anti-IL-17A and anti-IL-17RA antibody drugs secukinumab (Cosentyx), ixekizumab (Talz), and brodalumab (Siliq) in indications like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
The industry has even higher hopes for small molecule alternative antibody therapeutics as a result of the new research into small molecule conjugates for IL-17A. Traditional biological agents used to stop protein-protein interactions (PPIs) between cytokines and their receptors, such as interleukins, are cytokines and cytokine receptors. While a few businesses, including Ensemble, DiCE, and Eli Lilly, have submitted patent applications for small molecule IL-17A antagonists, LEO Pharma has the edge.

YourChoice Therapeutics'
YCT529, a possible non-hormonal male contraception with remarkable preclinical oral effectiveness, is anticipated to start clinical testing in the first half of 2023.
This retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR-) antagonist was initially identified at the Gunda Georg lab at the University of Minnesota. It was highlighted at the ACS 2022 Spring Conference and first reported data in 2022. Reversible oral male contraceptives have been difficult to develop for a number of reasons, including the strict safety requirements for dosage and the high standards of effectiveness compared to more well-established female contraceptive methods.
YCT529 should do well in terms of efficacy and side effects if it is as safe and efficacious in people. Male birth control pills are also hoped to provide both men and women additional alternatives to shoulder the duty of contraception, however there is still a long way to go before they can be formally commercialized.
The sole selective M4 PAM in clinical development is
emraclidine (enlaridine, CVL-231) (CAS 2170722-84-4), a PAM of the cholinergic M4 muscarinic receptor produced by Cerevel Therapeutics. Emraclidine is now undergoing multiple Phase II studies and is being considered for development in Alzheimer's disease after showing promising early results in schizophrenia. The establishment of several Phase II studies is now being suggested for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Emraclidine has demonstrated strong target engagement in PET investigations in non-human primates and is highly permeable to the brain. Emraclidine does not require concurrent inhibition of peripheral M1 receptors since it is extremely selective for M4 and has no discernible agonistic action on M1.
Emraclidine has an M4 selectivity 390 times higher than that of other muscarinic receptors. Emraclidine improved overall PANSS scores at week 6 compared to placebo in a recent phase 1b study in schizophrenia patients. This improvement was both clinically and statistically significant.

An oral selective complement 5a (C5a) receptor inhibitor called
avacopan(CAS 1346623-17-3) was authorized in 2021 to treat the uncommon autoimmune condition known as ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV).
Avacopan was initially created by ChemoCentryx, for which ViforPharma has been awarded an exclusive commercialization license outside of the United States. KISSEI Pharma has been given an exclusive license for development and marketing in Japan. Amgen purchased ChemoCentryx in 2022 for $4 billion in cash with the obvious goal of acquiring avacopan.
The receptor for the inflammatory complement subunit C5a, avacopan inhibits C5aR GPCR. Cyclophosphamide, a mustard agent often used in chemotherapy, is part of the standard of treatment for AAV, underlining a critical medical need in this context.











